The Broad Institute team led by Dan MacArthur announced the release of gnomAD version 2.1 at last year’s ASHG conference. This new version boasted data from 125,748 exomes and 15,708 genomes, but the greater updates were the improved QC refinement and more discrete sub-population break downs.
Although the majority of samples were counted in the previous 2.0.2 release, the additional samples passed through the QC pipeline improvements (like refined sex abnormality filters and excluding more ‘low call rate’ entries) did provide increased numbers of samples in the 2.1 release.
| Overlapping | Only in 2.0.2 | Only in 2.1 | |
| Genomes | 14,977 | 519 | 731 |
| Exomes | 119,116 | 4,020 | 6,632 |
The next big change was a larger draw, though, where the non-Finnish European and East Asian populations were broken down into sub-populations. These sub-population numbers are shown below.

The global and sub-continental ancestries were determined using PCA and random forest predictions which created the distinct clusters shown below.

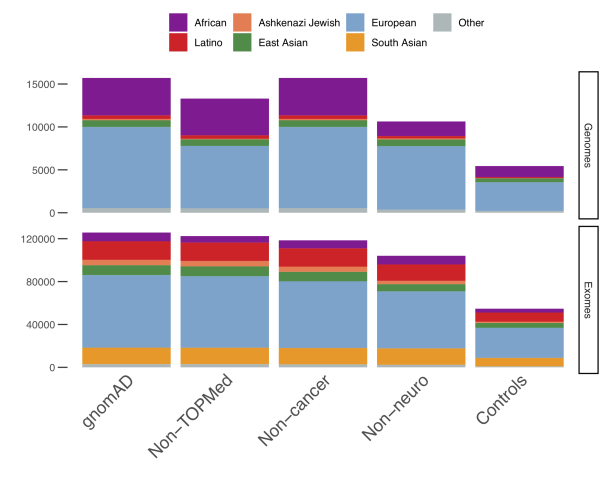
Finally, one more advantage is including the allele frequencies for controls-only subsets with no cases from common disease case/control studies (Controls), for samples not assessed for a neurological phenotype (Non-neuro), for samples that were not part of a cancer cohort (Non-cancer), and for samples that are not part of the TOPMed (Trans-Omics for Precision Medicine) dataset (Non-TOPMed). These controls will likely appeal to clinical users who want to increase the pool of common, non-detrimental alleles for comparison.
Golden Helix was very excited to get this new data, curate it, and provide it to customers, but during the process of curating, gnomAD v2.1.1 was released. Version 2.1.1 is a minor release where some of the filtering and annotating methods were tweaked. Nonetheless, we decided to forego a gnomAD 2.1 release, and jump right to a 2.1.1 release. Furthermore, since the new tracks provide such a variety of information, it was important to consider which sections to organize and keep for easy integration with previous workflows while optimizing which new fields to add. The new gnomAD 2.1.1 frequency track will include the controls groups and the sub-populations.
Although gnomAD is natively built with GRCh37 reference genome, we are keeping with our policy of releasing all annotations equally on the GRCh38 assemblies and used a combination of our LiftOver capability and carefully written frequency adjusting scripts for the few sites where the change in reference genome flip the reference and alternate alleles.
Look for this updated gnomAD 2.1.1 release today!